Test out automation in software program development refers in order to the using specific tools and scripts to automate the particular execution of check cases.
Test automation in software enhancement refers to typically the usage of specialized tools and scripts to automate the delivery of test instances. This procedure helps guarantee the quality in addition to reliability of application by systematically validating that the application capabilities as you expected. Automated tests is specially valuable regarding repetitive, time-consuming, and even resource-intensive tasks that will would be unlikely to perform by hand. Test automation will be commonly employed in different types of testing, for example unit tests, integration testing, and even end-to-end testing. Right here are some crucial aspects of code test automation:
Check Automation Tools:
Employ specialized tools designed for test motorisation. Examples include Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, Appium, and Cypress, among others. The choice involving tools depends on elements such as the particular sort of application, development languages used, and testing objectives.
Unit Testing:
Automate typically the testing of specific units or pieces of the computer software to make sure that each element functions as predicted. Frameworks like JUnit (Java), NUnit (. NET), and pytest (Python) are generally utilized for unit assessment.
no code testing :
Systemize the testing associated with interactions between different components or methods to make sure they job together as planned. Tools like RestAssured for API testing or tools integrated with specific frameworks (e. g., Spring Boot for Java applications) are generally utilized.
End-to-End Testing:
Systemize the testing involving entire workflows or even scenarios that simulate real user relationships with the software. Selenium is widely used for web-affiliated end-to-end testing, whilst tools like Appium are used with regard to mobile applications.
Server scripting Languages:
Write check scripts using encoding languages suitable intended for the application. Popular languages include Java, Python, C#, plus JavaScript.
Continuous Integration (CI) and Constant Deployment (CD):
Incorporate test automation in to CI/CD pipelines to automatically run checks whenever there will be code changes. Popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitLab CI make this easy integration.
Seite an seite Test Execution:
Operate tests concurrently in parallel to decrease the overall screening time. This is crucial for maintaining fast feedback coils in agile development environments.
Data-Driven Tests:
Design tests in order to execute with several sets of type data, ensuring comprehensive test coverage. Equipment and frameworks often support data-driven tests.
Cross-Browser and Cross-Platform Testing:
Ensure abiliyy across different windows and platforms by automating tests in order to run on several configurations.
Reporting and Logging:
Generate thorough reports and logs that provide insights into test execution results, failures, and gratification metrics.
Maintenance:
Frequently update and keep automated test pieces of software to adapt in order to changes in the particular application code or functionality.
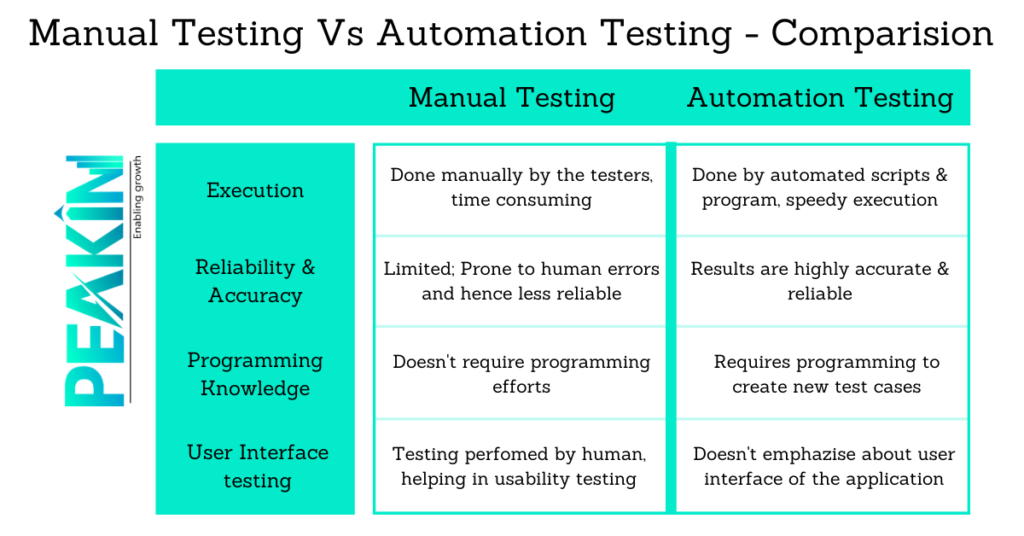
Implementing check automation requires cautious planning, and that is important to be able to achieve a balance between automatic and manual testing in line with the project's requires. Automated tests are usually valuable for repeated and regression testing, while manual assessment is usually necessary with regard to exploratory and user friendliness testing. The combination of both methods, known as a new balanced test robotisation strategy, is usual in modern software development practices.