From Concept to Creation: Unleashing the Power of Molds in Plastic Manufacturing
In the world of manufacturing, molds for plastic serve as a catalyst for innovation and efficiency. From the simplest household items to complex machinery parts, molds play a crucial role in shaping the products we use every day. The process begins with an idea, which is brought to life through meticulous design and engineering, ultimately resulting in the creation of molds that define the final shape, texture, and functionality of plastic items.
Understanding the significance of molds in plastic manufacturing opens up a realm of possibilities for businesses and designers alike. The precision and versatility of molds allow for mass production of intricate designs while maintaining uniform quality. As we explore the various applications and advancements in mold technology, it becomes clear that these tools are not just about shaping materials, but about unleashing creativity and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in plastic production.
Understanding Mold Design
The design of molds for plastic manufacturing is a critical step in ensuring the success of the production process. A well-designed mold can significantly enhance the efficiency and quality of the final product. Key considerations in mold design include the type of plastic to be used, the part's geometry, and the production volume. Each of these factors influences the choice of materials for the mold and its configuration, affecting how heat is transferred and how the plastic flows during the injection molding process.
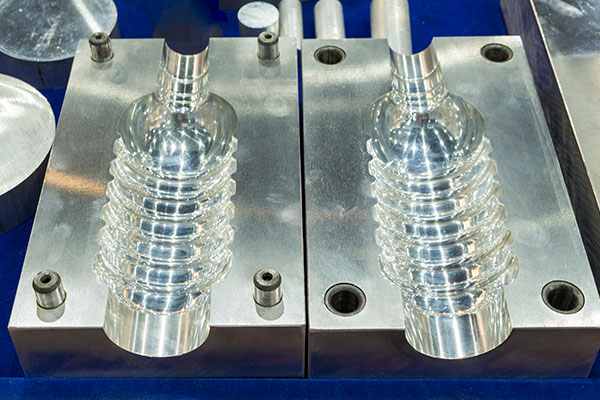
Another essential aspect of mold design is the incorporation of features that facilitate the release of the finished product. Draft angles, which are subtle inclines added to the vertical walls of the mold, allow the molded part to be removed more easily. Venting systems are also important; they enable trapped air to escape during the injection process, preventing defects such as air bubbles or incomplete filling. These design elements are crucial for producing parts that not only meet strict dimensional tolerances but also exhibit high-quality surface finishes.
Furthermore, the durability of the mold plays a substantial role in the overall cost-effectiveness of plastic manufacturing. Molds are subjected to intense pressure and temperature fluctuations during the production cycle, so selecting appropriate materials, including hardened steels or aluminum, is essential for achieving a longer lifespan. Innovative design techniques, such as conformal cooling channels, can also be integrated to optimize thermal management, reducing cycle times and improving the quality of the molded parts. Understanding these design principles is vital for manufacturers aiming to leverage molds in plastic production effectively.
Types of Molds Used in Plastic Manufacturing
In plastic manufacturing, the type of mold used can significantly affect the quality and efficiency of the production process. One of the most common types is the injection mold, which allows molten plastic to be injected into a precisely shaped cavity. This method is highly efficient for mass production, enabling manufacturers to create complex shapes and detailed designs with a smooth finish. Injection molds are typically made from high-strength steel or aluminum, which can withstand the pressures of the injection process and provide durability for long-term use.
Another popular mold type is the blow mold, primarily used for producing hollow plastic products, such as bottles and containers. The blow molding process involves forming a molten tube of plastic, called a parison, which is then inflated into the desired shape by air pressure. This method is particularly advantageous for producing lightweight containers and packaging while minimizing material waste. Blow molds can be designed for both single-use and reusable products, making them versatile for various applications across industries.
Thermoforming molds are also essential in plastic manufacturing, especially for creating larger products or sheets. This process involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes pliable, then draping it over a mold and allowing it to cool to retain the shape. Thermoforming is often used for applications like packaging, automotive interior components, and recreational products. The flexibility and scalability of thermoforming molds make them ideal for both small-scale and large-scale production runs, catering to the diverse needs of manufacturers.
The Process of Mold Production
The production of molds for plastic begins with meticulous design and engineering, which are crucial steps in ensuring the final product meets specifications. Designers utilize advanced software to create detailed 3D models that represent the desired shape and features of the plastic part. Considerations such as material flow, cooling channels, and ejection mechanisms are factored into the design to enhance the mold's performance and efficiency during the injection molding process.
Once the design is finalized, the next stage is manufacturing the mold itself. This process involves several techniques, including CNC machining, electrical discharge machining, and 3D printing, depending on the complexity and requirements of the mold. The selected materials for mold construction often include high-grade steel or aluminum, chosen for their durability and ability to withstand the pressures and temperatures associated with plastic molding operations. Precision is key, as even the slightest inaccuracies can lead to flawed production.
After the mold is created, rigorous testing and quality checks are performed to ensure that it functions correctly with the intended plastic material. This includes running trial injections to identify any potential issues, such as warping or incomplete filling of the mold cavities. Once the mold passes all evaluations, it is ready for full-scale production, paving the way for a wide array of plastic products that can be produced consistently and efficiently.