The Art of Precision: Mastering Molds for Injection Molding
In the world of manufacturing, molds play a pivotal role in the process of injection molding. These precision tools are the unsung heroes behind the creation of a wide array of everyday products, from car parts to packaging containers. Mastering the art of molds for injection molding is essential for achieving high-quality, consistent results in production. Let's delve into the intricacies of molds and explore how they are central to the success of injection molding processes.
Types of Injection Molding Molds
There are primarily four types of molds commonly used in injection molding: cold runner molds, hot runner molds, insulated runner molds, and multi-cavity molds. Each type has its own unique characteristics that cater to different molding requirements. Cold runner molds are cost-effective, but they tend to produce more waste material. Hot runner molds, on the other hand, are efficient in reducing material wastage and are often used for high-volume production runs.
Insulated runner molds are a specialized type of mold that helps in minimizing energy consumption during the injection molding process. They are designed to maintain the temperature of the molten material, leading to improved efficiency and quality of the finished products. Multi-cavity molds are used when multiple identical parts need to be produced simultaneously. This type of mold increases production output and helps in achieving economies of scale.
Choosing the right type of injection molding mold is crucial in ensuring the success of a manufacturing project. Factors such as material properties, part design complexity, production volume, and budget constraints should all be taken into consideration when selecting the appropriate mold type for a specific application. By understanding the characteristics and advantages of each mold type, manufacturers can optimize their injection molding processes for enhanced productivity and cost-effectiveness.
Design Considerations for Molds
When designing molds for injection molding, one crucial factor to consider is the material selection. The chosen material should have the right combination of properties, including heat resistance, toughness, and dimensional stability, to ensure the mold can withstand the rigors of the injection molding process.
Another important consideration is the mold geometry. Designing the mold with proper gating and cooling channel layouts is essential for achieving uniform filling, reducing cycle times, and minimizing defects. Additionally, draft angles and wall thickness uniformity play a key role in facilitating part ejection and maintaining structural integrity.
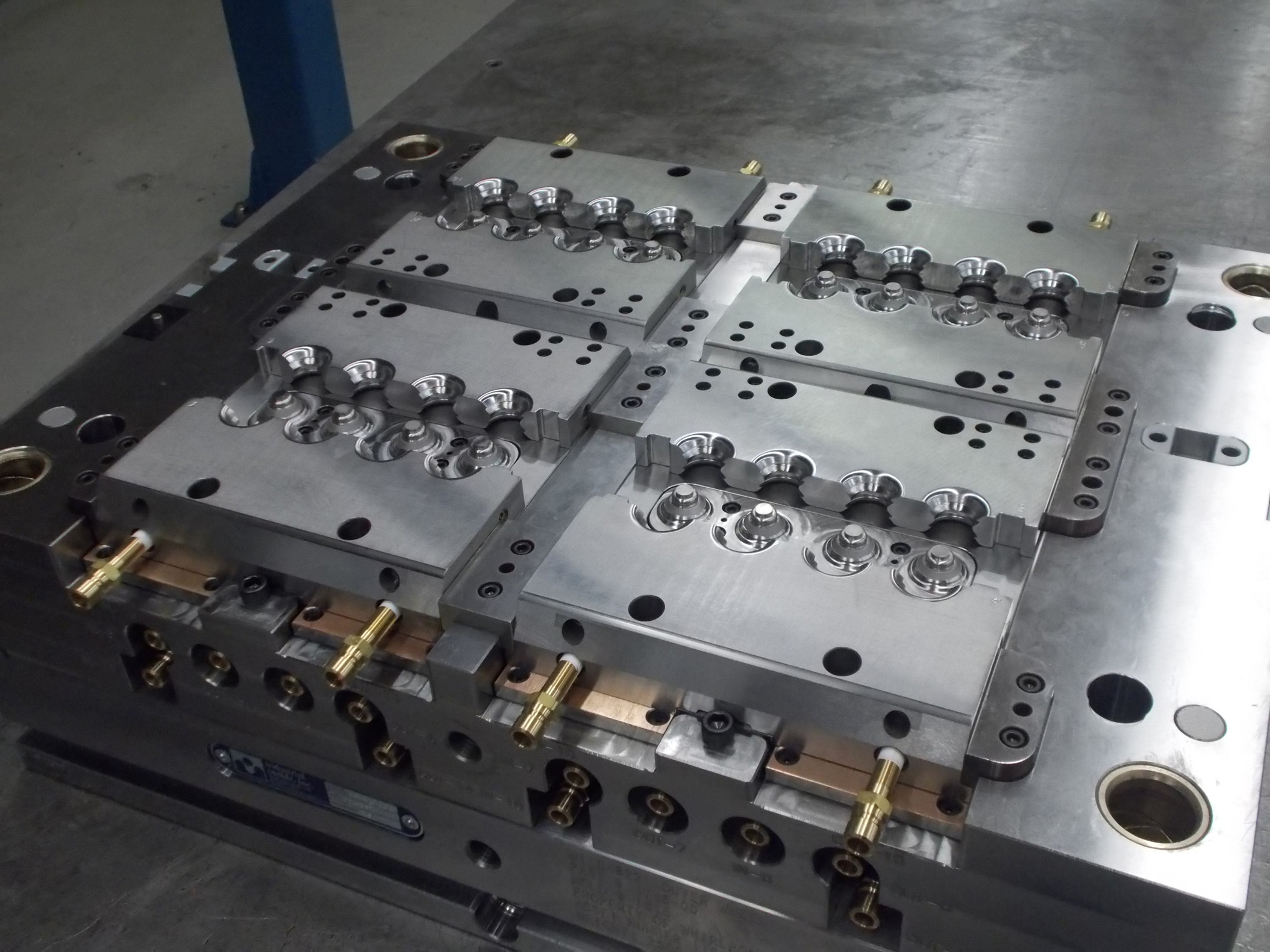
Furthermore, venting is a critical aspect of mold design that is often overlooked. Proper venting enables the escape of air and gases during the molding process, preventing defects such as burns or voids in the final parts. Attention to detail in venting design can significantly improve the overall quality of injection-molded products.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Proper maintenance of molds is crucial to ensure consistent production quality. Regular cleaning and inspection help prevent defects and prolong the lifespan of the molds. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for maintenance schedules and procedures.
When troubleshooting mold issues, start by identifying the root cause of the problem. Common issues include flashing, sink marks, and warping. By analyzing the production process and examining the molds, you can pinpoint the source of the problem and take corrective actions to address it effectively.
Incorporating preventive maintenance practices can minimize downtime and maximize productivity. Implement a maintenance log to track cleaning schedules, repairs, and performance evaluations. Regularly monitoring the molds' condition and addressing any issues promptly will optimize the injection molding process.